Nursing care for nephrotic syndrome plays a vital role in managing this complex condition, characterized by excessive protein loss in the urine. This article provides a comprehensive overview of nephrotic syndrome, its clinical manifestations, nursing assessment, care plan, medications, dietary management, patient education, and monitoring.
Understanding the pathophysiology, symptoms, and nursing interventions associated with nephrotic syndrome is crucial for effective patient care. This guide aims to empower nurses with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide holistic and evidence-based care for individuals with nephrotic syndrome.
1. Definition and Overview
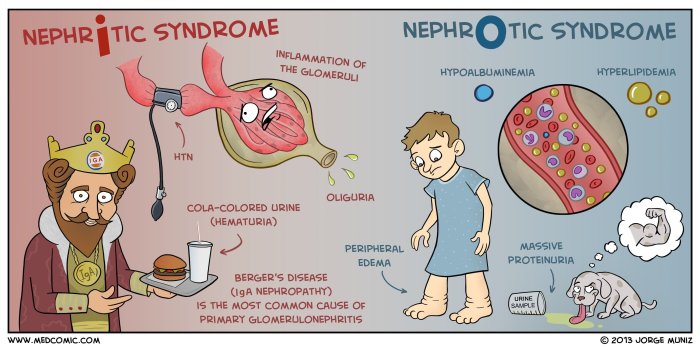
Nephrotic syndrome is a clinical condition characterized by excessive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and edema. It is caused by damage to the glomerular filtration barrier, leading to the leakage of large amounts of protein into the urine.
2. Clinical Manifestations
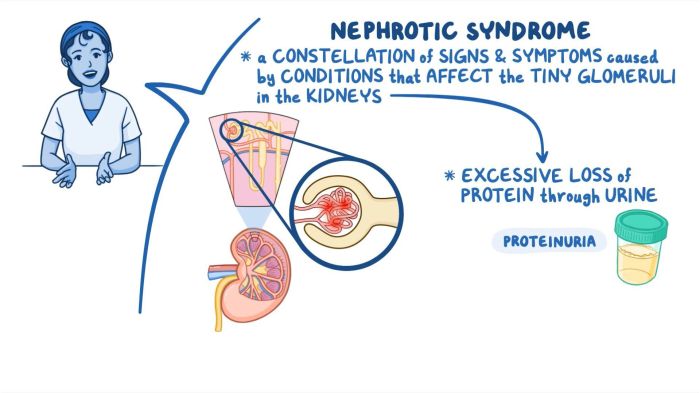
The classic signs and symptoms of nephrotic syndrome include:
- Proteinuria (excessive protein in the urine)
- Hypoalbuminemia (low levels of albumin in the blood)
- Edema (swelling in the face, hands, feet, and abdomen)
- Hyperlipidemia (elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood)
- Thromboembolic events (increased risk of blood clots)
3. Nursing Assessment
Nursing assessment for patients with nephrotic syndrome includes:
- Monitoring vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature)
- Assessing fluid balance (intake and output)
- Examining for edema (location, severity, and pitting)
- Evaluating skin integrity (dryness, itching, and excoriation)
- Monitoring laboratory values (urinalysis, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and albumin)
4. Nursing Care Plan

The nursing care plan for patients with nephrotic syndrome focuses on:
- Managing edema (diuretics, sodium restriction, and elevation of extremities)
- Preventing complications (anticoagulants, antibiotics, and immunizations)
- Promoting well-being (skin care, rest, and emotional support)
- Educating patients about the disease and its management
5. Medications and Treatments
Medications used to treat nephrotic syndrome include:
- Diuretics (to reduce edema)
- Sodium restriction (to reduce fluid retention)
- Anticoagulants (to prevent blood clots)
- Immunosuppressants (to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation)
6. Dietary Management: Nursing Care For Nephrotic Syndrome
Dietary management is crucial in nephrotic syndrome to:
- Restrict sodium intake (to reduce edema)
- Limit protein intake (to reduce proteinuria)
- Restrict fluid intake (to prevent fluid overload)
7. Patient Education and Support
Patient education and support are essential for managing nephrotic syndrome:
- Explaining the disease and its management
- Teaching self-management techniques (monitoring weight, blood pressure, and urine protein)
- Emphasizing medication adherence
- Promoting lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, and smoking cessation)
8. Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring the effectiveness of nursing care includes:
- Regular follow-up appointments
- Laboratory tests (urinalysis, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and albumin)
- Assessment of edema and other symptoms
- Patient feedback on symptom management and well-being
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary cause of nephrotic syndrome?
The primary cause of nephrotic syndrome is damage to the glomerular filtration barrier, which allows excessive protein to leak into the urine.
What are the common signs and symptoms of nephrotic syndrome?
Common signs and symptoms include edema (swelling), proteinuria (excessive protein in the urine), hypoalbuminemia (low blood albumin levels), and hyperlipidemia (elevated blood lipid levels).
What is the role of nurses in managing nephrotic syndrome?
Nurses play a crucial role in assessing, planning, implementing, and evaluating nursing care for patients with nephrotic syndrome. They monitor vital signs, fluid balance, and other relevant parameters, provide patient education, and coordinate interdisciplinary care.